Cross-layer equalization¶
Context¶
Quantization of floating point models into lower bitwidths introduces quantization noise on the weights and activations, which often leads to reduced model performance. To minimize quantization noise, there are a variety of post training quantization (PTQ) techniques offered by AIMET. You can learn more about these techniques here.
AIMET’s cross-layer equalization tool involves the following techniques:
Batch Norm Folding: This feature folds batch norm layers into adjacent convolutional and linear layers. You can learn more here
Cross Layer Scaling: In some models, the parameter ranges for different channels in a layer show a wide variance (as shown below). This feature attempts to equalize the distribution of weights per channel of consecutive layers. Thus, different channels have a similar range and the same quantization parameters can be used for weights across all channels.
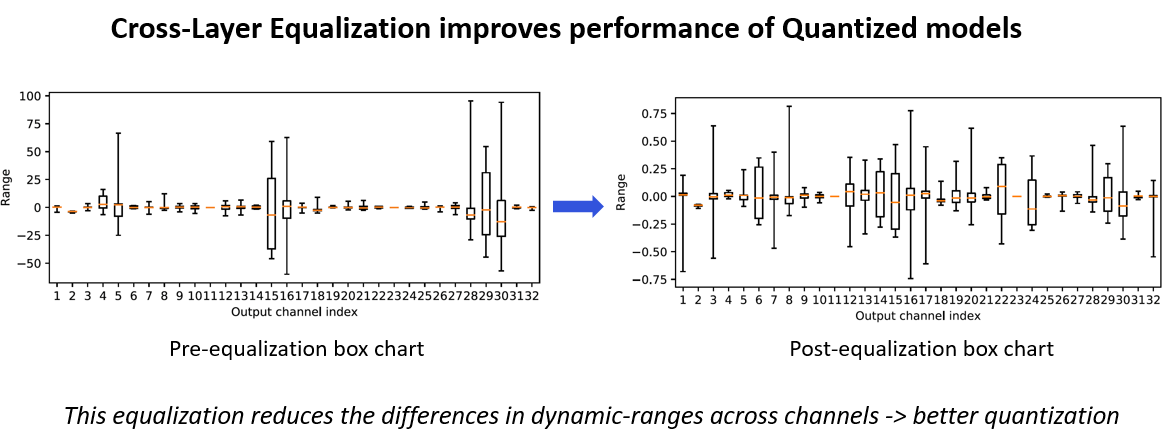
High Bias Fold: Cross layer scaling may result in high bias parameter values for some layers. This technique folds some of the bias of a layer into the subsequent layer’s parameters. This feature requires batch norm parameters to operate on and will not be applied otherwise.
Workflow¶
Setup¶
import torch
from torchvision.models import mobilenet_v2
# General setup that can be changed as needed
device = "cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
model = mobilenet_v2(pretrained=True).eval().to(device)
input_shape = (1, 3, 224, 224)
Load the model for cross-layer equalization. In this code example, we will use MobileNetV2.
It’s recommended to apply the TensorFlow prepare_model API before applying AIMET functionalities. After preparation, we find that the model contains consecutive convolutions, which can be optimized through cross-layer equalization.
from aimet_tensorflow.keras.cross_layer_equalization import equalize_model
from aimet_tensorflow.keras.model_preparer import prepare_model
from tensorflow.keras import applications
model = applications.MobileNetV2()
print(model.summary())
prepared_model = prepare_model(model)
print('*** Before cross-layer equalization ***')
print('\nprepared_model.layers[1]:')
print(type(prepared_model.layers[1]))
print('\nprepared_model.layers[4]:')
print(type(prepared_model.layers[4]))
print('\nPrev Conv weight')
print(prepared_model.layers[1].get_weights()[0])
print('\nNext Conv weight')
print(prepared_model.layers[4].get_weights()[0])
Model: "mobilenetv2_1.00_224"
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param # Connected to
==================================================================================================
input_1 (InputLayer) [(None, 224, 224, 3 0 []
)]
Conv1 (Conv2D) (None, 112, 112, 32 864 ['input_1[0][0]']
)
bn_Conv1 (BatchNormalization) (None, 112, 112, 32 128 ['Conv1[0][0]']
)
Conv1_relu (ReLU) (None, 112, 112, 32 0 ['bn_Conv1[0][0]']
)
expanded_conv_depthwise (Depth (None, 112, 112, 32 288 ['Conv1_relu[0][0]']
wiseConv2D) )
...
*** Before cross-layer equalization ***
prepared_model.layers[1]:
<class 'keras.layers.convolutional.conv2d.Conv2D'>
prepared_model.layers[4]:
<class 'keras.layers.convolutional.depthwise_conv2d.DepthwiseConv2D'>
Prev Conv weight
[[[[-1.71659231e-01 -3.33731920e-01 5.30122258e-02 -5.93232973e-21
2.08742931e-01 -1.20433941e-01 1.75700430e-02 -3.10708203e-22
-9.62498877e-03 1.90229788e-01 -3.67278278e-01 3.95997976e-22
...
3.87471542e-02 -3.67677957e-02 -3.23011987e-02 -4.83861901e-02
1.23156421e-02 -5.57984132e-03 -6.53976866e-04 -1.92511864e-02
-2.09685047e-22 1.19186290e-01 -2.52912678e-02 2.02078857e-02]]]]
Next Conv weight
[[[[-9.15259957e-01]
[ 6.11176670e-01]
[-4.27415752e+00]
...
[-1.17871511e+00]
[ 2.55578518e+00]
[ 3.69716495e-01]]]]
Load the model for cross-layer equalization. In this code example, we will convert PyTorch MobileNetV2 to ONNX and use it in the subsequent code.
It’s recommended to simplify the ONNX model before applying AIMET functionalities. After simplification, we find that the model contains consecutive convolutions, which can be optimized through cross-layer equalization.
import os
import onnx
import onnxsim
import torch
from aimet_onnx.cross_layer_equalization import equalize_model
from torchvision.models import MobileNet_V2_Weights, mobilenet_v2
pt_model = mobilenet_v2(weights=MobileNet_V2_Weights.DEFAULT)
print(pt_model)
# Shape for each ImageNet sample is (3 channels) x (224 height) x (224 width)
input_shape = (1, 3, 224, 224)
dummy_input = torch.randn(input_shape)
# Modify file_path as you wish, we are using temporary directory for now
file_path = os.path.join('/tmp', f'mobilenet_v2.onnx')
torch.onnx.export(
pt_model,
(dummy_input,),
file_path,
)
# Load exported ONNX model
model = onnx.load_model(file_path)
# Simplifying the model
try:
model, _ = onnxsim.simplify(model)
except:
print('ONNX Simplifier failed. Proceeding with unsimplified model')
initializers = {init.name: init for init in model.graph.initializer}
prev_conv_weight = onnx.numpy_helper.to_array(
initializers[model.graph.node[4].input[1]]
)
next_conv_weight = onnx.numpy_helper.to_array(
initializers[model.graph.node[5].input[1]]
)
print("*** Before cross-layer equalization ***")
print("\nmodel.graph.node[4]:")
print(model.graph.node[4].name)
print("\nmodel.graph.node[5]:")
print(model.graph.node[5].name)
print("\nPrev Conv weight")
print(prev_conv_weight)
print("\nNext Conv weight")
print(next_conv_weight)
MobileNetV2(
(features): Sequential(
(0): Conv2dNormActivation(
(0): Conv2d(3, 32, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(2, 2), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(1): BatchNorm2d(32, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(2): ReLU6(inplace=True)
)
...
)
*** Before cross-layer equalization ***
model.graph.node[4]:
/features/features.1/conv/conv.1/Conv
model.graph.node[5]:
/features/features.2/conv/conv.0/conv.0.0/Conv
Prev Conv weight
[[[[ 1.83640555e-01]]
[[ 6.34215236e-01]]
[[ 8.44993666e-02]]
...
[[-6.70130579e-17]]
[[-1.37757687e-02]]
[[ 9.16839484e-03]]]]
Next Conv weight
[[[[-8.41059163e-02]]
[[-1.12039044e-01]]
[[-2.72468403e-02]]
...
[[ 9.46642041e-01]]
[[ 4.35139937e-03]]
[[ 2.57021021e-02]]]]
Step 1¶
Execute AIMET cross-layer equalization API
from aimet_torch.cross_layer_equalization import equalize_model
# Performs BatchNorm folding, cross layer scaling and high bias folding
equalize_model(model, input_shape)
Execute AIMET cross-layer equalization API
cle_applied_model = equalize_model(prepared_model)
print('*** After cross-layer equalization ***')
print('\nPrev Conv weight')
print(cle_applied_model.layers[1].get_weights()[0])
print('\nNext Conv weight')
print(cle_applied_model.layers[3].get_weights()[0])
*** After cross-layer equalization ***
Prev Conv weight
[[[[-3.01457286e-01 -1.49024737e+00 6.10569119e-01 -1.29590677e-19
1.51547194e-01 -1.51446089e-01 1.38100997e-01 -4.89249423e-21
-5.16245179e-02 4.64579314e-01 -2.44408584e+00 1.22219264e-20
...
1.67510852e-01 -2.60713138e-02 -1.05549544e-01 -2.53403008e-01
1.39502389e-02 -1.54620111e-02 -1.97294299e-02 -9.41715762e-02
-6.88260233e-21 8.95088911e-02 -1.87630311e-01 2.48399768e-02]]]]
Next Conv weight
[[[[-1.00347728e-01]
[ 6.30402938e-02]
[-9.67416465e-01]
...
[-7.88373709e-01]
[ 6.75162792e-01]
[ 1.48045555e-01]]]]
Execute AIMET cross-layer equalization API
# Cross-layer equalization is working as in-place manner
equalize_model(model=model)
prev_conv_weight = onnx.numpy_helper.to_array(
initializers[model.graph.node[4].input[1]]
)
next_conv_weight = onnx.numpy_helper.to_array(
initializers[model.graph.node[5].input[1]]
)
print("*** After cross-layer equalization ***")
print("\nPrev Conv weight")
print(prev_conv_weight)
print("\nNext Conv weight")
print(next_conv_weight)
*** After cross-layer equalization ***
Prev Conv weight
[[[[ 6.28238320e-02]]
[[ 2.16966406e-01]]
[[ 2.89074164e-02]]
...
[[-2.44632760e-17]]
[[-5.02887694e-03]]
[[ 3.34694423e-03]]]]
Next Conv weight
[[[[-2.4585028e-01]]
[[-3.5856506e-01]]
[[-3.3467390e-02]]
...
[[ 1.2930528e+00]]
[[ 1.6213797e-02]]
[[ 7.0406616e-02]]]]
API¶
Top-level API
- aimet_torch.cross_layer_equalization.equalize_model(model, input_shapes=None, dummy_input=None)[source]¶
High-level API to perform Cross-Layer Equalization (CLE) on the given model. The model is equalized in place.
- Parameters:
model (
Module) – Model to equalizeinput_shapes (
Union[Tuple,List[Tuple],None]) – Shape of the input (can be a tuple or a list of tuples if multiple inputs)dummy_input (
Union[Tensor,Tuple,None]) – A dummy input to the model. Can be a Tensor or a Tuple of Tensors. dummy_input will be placed on CPU if not already.
Top-level API