Migrate to aimet_torch.v2
Learn how to migrate your code from aimet_torch v1 to aimet_torch v2!
Migration to aimet_torch v2 enables access to new features, easier debugging, and simpler code that is easier to extend. This guide provides an overview of the migration process and describes the fundamental differences between the two versions.
Note
Please be advised that aimet_torch v2 is an experimental feature whose APIs and behaviors are subject to change.
Changes in aimet_torch v2
Before migrating, it is important to understand the behavior and API differences between aimet_torch v1 and aimet_torch v2. Users can interact with aimet_torch through the high level APIs in the same way. Methods like compute_encodings() and export() will remain the same.
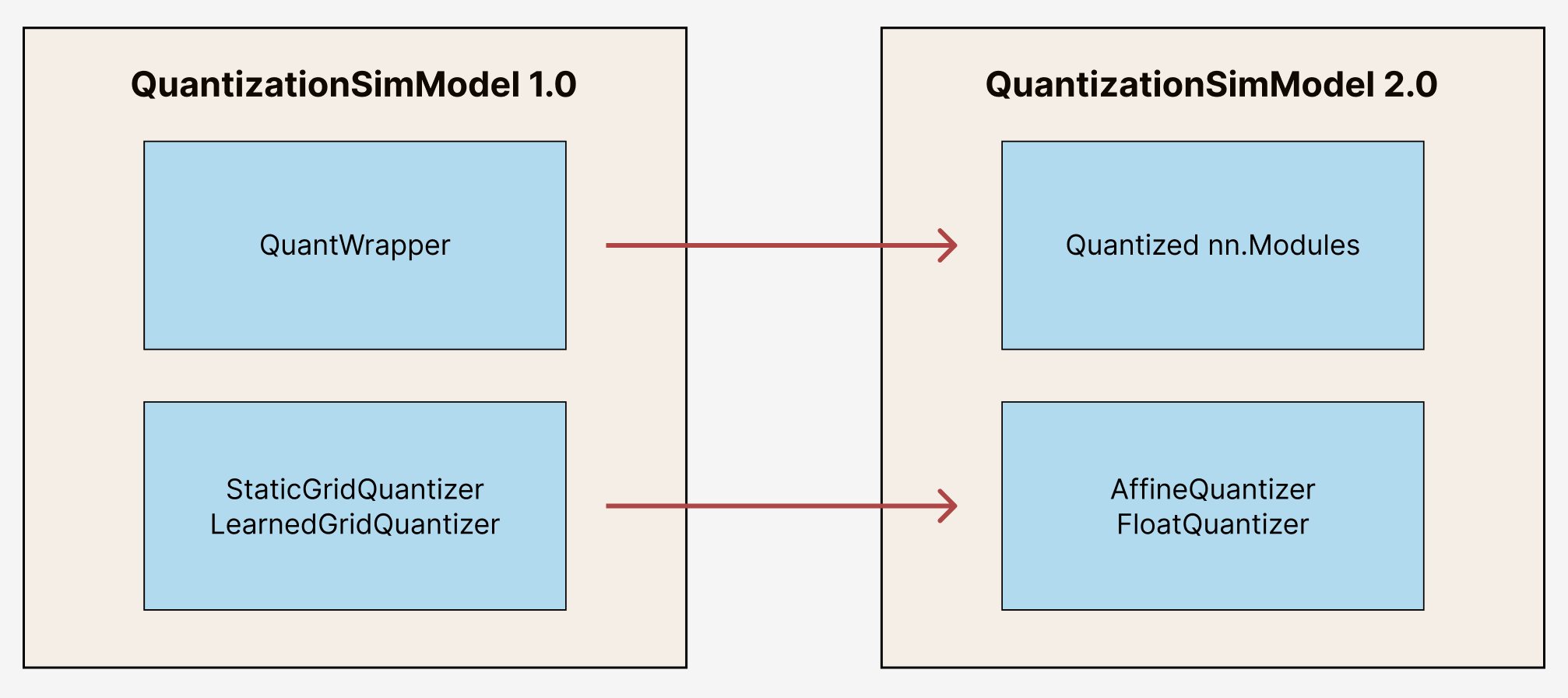
Under the hood, aimet_torch v2 has a different set of building blocks and properties than aimet_torch v1, as shown below:
Migration Process
The migration process includes the following:
Update imports of QuantizationSimModel and other features
Change how internal components of QuantizationSimModel are accessed
Remove any dependency on deprecated features
Imports
To migrate to aimet_torch v2, your imports should originate from the aimet_torch.v2 namespace and be replaced as shown below. If your code does not directly access lower-level components, no further code change is needed.
AIMET Classes |
|
|
|---|---|---|
QuantSim |
|
|
AdaRound |
|
|
Sequential MSE |
|
|
QuantAnalyzer |
|
|
All the other import statements will stay the same, including but not limited to:
from aimet_common.defs import QuantSchemefrom aimet_torch.cross_layer_equalization import equalize_modelfrom aimet_torch.model_preparer import prepare_model
QuantizationSimModel
Moving from QuantWrapper to Quantized Modules
To enable quantization in aimet_torch v1, modules are wrapped with a QuantizeWrapper. These wrapped modules can be accessed as follows:
from aimet_torch.quantsim import QuantizationSimModel as QuantizationSimModelV1
sim = QuantizationSimModelV1(...)
all_quant_wrappers = sim.quant_wrappers()
for quant_wrapper in sim.quant_wrappers():
print(quant_wrapper)
StaticGridQuantWrapper(
(_module_to_wrap): Linear(in_features=100, out_features=200, bias=True)
)
StaticGridQuantWrapper(
(_module_to_wrap): ReLU()
)
In contrast, aimet_torch v2 enables quantization through quantized nn.Modules - modules are no longer wrapped but replaced with a quantized version. For example, a nn.Linear would be replaced with QuantizedLinear, nn.Conv2d would be replace by QuantizedConv2d, and so on. The quantized module definitions can be found under aimet_torch.v2.nn. These quantized modules can be accessed as follows:
from aimet_torch.v2.quantsim.quantsim import QuantizationSimModel as QuantizationSimModelV2
sim2 = QuantizationSimModelV2(...)
all_q_modules = sim2.qmodules()
for q_module in sim2.qmodules():
print(q_module)
QuantizedLinear(
in_features=100, out_features=200, bias=True
(param_quantizers): ModuleDict(
(weight): QuantizeDequantize(shape=[1], bitwidth=8, symmetric=True)
(bias): None
)
(input_quantizers): ModuleList(
(0): QuantizeDequantize(shape=[1], bitwidth=8, symmetric=False)
)
(output_quantizers): ModuleList(
(0): None
)
)
QuantizedReLU(
(param_quantizers): ModuleDict()
(input_quantizers): ModuleList(
(0): None
)
(output_quantizers): ModuleList(
(0): QuantizeDequantize(shape=[1], bitwidth=8, symmetric=False)
)
)
For more information on Quantized modules, please refer to the API reference guide here.
Moving from StaticGrid and LearnedGrid Quantizer to Affine and Float Quantizer
In aimet_torch v1, we relied on StaticGridQuantizer and LearnedGridQuantizer. For both, floating point quantization could be enabled based on QuantizationDataType passed in.
from aimet_torch.v1.tensor_quantizer import StaticGridPerChannelQuantizers
from aimet_common.defs import QuantizationDataType
fp_quantizer = StaticGridPerChannelQuantizer(data_type = QuantizationDataType.float, ...)
affine_quantizer = StaticGridPerChannelQuantizer(data_type = QuantizationDataType.int, ...)
However, in aimet_torch v2, this functionality is separated into an AffineQuantizer and a FloatQuantizer. Users can access these quantizers and related operations under aimet_torch.v2.quantization.
import aimet_torch.v2.quantization as Q
affine_q = Q.affine.Quantize(shape=(5, 1), bitwidth=8, symmetric=False)
affine_qdq = Q.affine.QuantizeDequantize(shape=(5, 1), bitwidth=8, symmetric=False)
fp_qdq = Q.float.FloatQuantizeDequantize(dtype=torch.float16)
From the wrapped module (aimet_torch v1) or quantized module (aimet_torch v2), the attributes to access the quantizers remain consistent: .input_quantizers for input quantizers, .output_quantizers for output quantizers, and .param_quantizers for parameter quantizers.
For more information on Quantizers, please refer to the API reference guide here.
Code Examples
Setup
# aimet_torch v1
from aimet_torch.quantsim import QuantizationSimModel as QuantizationSimModelV1
sim1 = QuantizationSimModelV1(...)
wrap_linear = sim1.model.linear
# aimet_torch v2
from aimet_torch.v2.quantsim.quantsim import QuantizationSimModel as QuantizationSimModelV2
sim2 = QuantizationSimModelV2(...)
qlinear = sim2.model.linear
Case 1: Manually setting common attributes
Bitwidth
# aimet_torch v1
wrap_linear.param_quantizers['weight'].bitwidth = 4
wrap_linear.input_quantizers[0].bitwidth = 4
wrap_linear.output_quantizers[0].bitwidth = 4
# aimet_torch v2
if qlinear.param_quantizers['weight']:
module.param_quantizers['weight'].bitwidth = 4
if qlinear.input_quantizers[0]:
qlinear.input_quantizers[0].bitwidth = 4
if qlinear.output_quantizers[0]:
qlinear.output_quantizers[0].bitwidth = 4
Symmetry
# aimet_torch v1
wrap_linear.param_quantizers['weight'].use_symmetric_encodings = True
wrap_linear.param_quantizers['weight'].is_unsigned_symmetric = False
wrap_linear.param_quantizers['weight'].use_strict_symmetric = False
wrap_linear.input_quantizers[0].use_symmetric_encodings = True
wrap_linear.input_quantizers[0].is_unsigned_symmetric = False
wrap_linear.input_quantizers[0].use_strict_symmetric = False
wrap_linear.output_quantizers[0].use_symmetric_encodings = True
wrap_linear.output_quantizers[0].is_unsigned_symmetric = False
wrap_linear.output_quantizers[0].use_strict_symmetric = False
# aimet_torch v2
# Notes: simplified into two flags
if qlinear.param_quantizers['weight']:
qlinear.param_quantizers['weight'].symmetric = True
qlinear.param_quantizers['weight'].signed = True
if qlinear.input_quantizers[0]:
qlinear.input_quantizers[0].symmetric = True
qlinear.input_quantizers[0].signed = True
if qlinear.output_quantizers[0]:
qlinear.output_quantizers[0].symmetric = True
qlinear.output_quantizers[0].signed = True
Encoding Data
# aimet_torch v1
import libpymo
if wrap_linear.param_quantizers['weight'].encoding:
encoding = libpymo.TfEncoding()
encoding.max = 1
encoding.min = -1
wrap_linear.param_quantizers['weight'].encoding = encoding
if wrap_linear.input_quantizers[0].encoding:
encoding = libpymo.TfEncoding()
encoding.max = 1
encoding.min = -1
wrap_linear.input_quantizers[0].encoding = encoding
if wrap_linear.output_quantizers[0].encoding:
encoding = libpymo.TfEncoding()
encoding.max = 1
encoding.min = -1
wrap_linear.output_quantizers[0].encoding = encoding
# aimet_torch v2
# Notes: TfEncoding() is no longer used, encoding min/max are of type torch.nn.Parameter
if qlinear.param_quantizers['weight']:
qlinear.param_quantizers['weight'].min.copy_(-1.0)
module.param_quantizers['weight'].max.copy_(1.0)
if qlinear.input_quantizers[0]:
qlinear.input_quantizers[0].min.copy_(-1.0)
qlinear.input_quantizers[0].max.copy_(1.0)
if qlinear.output_quantizers[0]:
qlinear.output_quantizers[0].min.copy_(-1.0)
qlinear.output_quantizers[0].max.copy_(1.0)
Case 2: Enabling and Disabling Quantization
Is quantization enabled?
# aimet_torch v1
if wrap_linear.param_quantizers['weight'].enabled:
pass
# aimet_torch v2
# Notes: Quantizers no longer have an 'enabled' attribute. If a quantizer is present, it is enabled
if qlinear.param_quantizers['weight']:
pass
Disabling Quantization
# aimet_torch v1
wrap_linear.param_quantizers['weight'].enabled = False
# aimet_torch v2
# Notes: Quantizers can be disabled by setting them to None OR using the utility API (_remove_input_quantizers, _remove_output_quantizers, _remove_param_quantizers)
qlinear.param_encodings["weight"] = None
qlinear._remove_param_quantizers('weight')
Enabling Quantization
# aimet_torch v1
wrap_linear.param_quantizers['weight'].enabled = True
# aimet_torch v2
import aimet_torch.v2.quantization as Q
qlinear.param_quantizers['weight'] = Q.affine.QuantizeDequantize(...)
Temporarily disabling Quantization
# aimet_torch v1
assert wrap_linear.param_quantizers['weight'].enabled
wrap_linear.param_quantizers['weight'].enabled = False
# Run other code here
wrap_linear.param_quantizers['weight'].enabled = True
# aimet_torch v2
assert qlinear.param_quantizers['weight']
with qlinear._remove_param_quantizers('weight'):
assert qlinear.param_quantizers['weight'] is None
# Run other code here
assert qlinear.param_quantizers['weight']
Case 3: Freezing encodings
# aimet_torch v1
if not wrap_linear.param_quantizers['weight']._is_encoding_frozen:
wrap_linear.param_quantizers['weight'].freeze_encodings()
# aimet_torch v2
# Notes: There is no longer a concept of "freezing". Mimicking v1 freezing behavior involves the allow_overwrite and requires_grad_ flag
qlinear.param_quantizers['weight'].allow_overwrite(False) # Prevents encodings from being overwritten by AIMET APIs
qlinear.param_quantizers['weight'].requires_grad_(False) # Prevents encodings from being learned