AIMET greedy compression ratio selection
Overview
Spatial SVD and channel pruning (CP) work on individual layers of a model. Not all the layers are equally compressible, so compression of a given layer has a variable impact on the final model accuracy. The greedy per-layer compression ratio selection algorithm assesses the sensitivity of layers to compression and finds an appropriate compression ratio for each layer. The algorithm ensures that the model maintains the highest possible accuracy while meeting the target compression ratio.
How it works
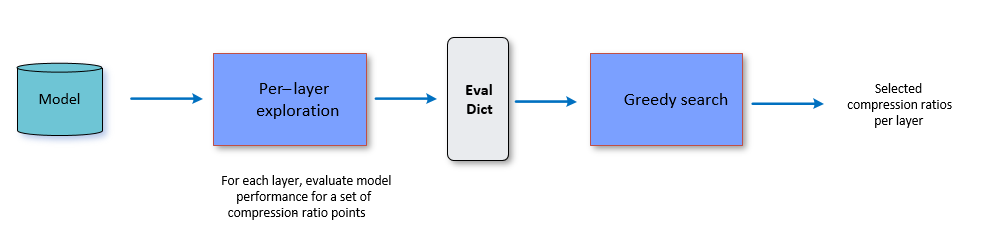
The greedy compression ratio selection algorithm works in two steps:
Per-layer exploration
Compression-ratio selection
Inputs to the process include:
The original model
An evaluation function that produces a single performance number
A target compression ratio
A pruning method (channel pruning, spatial SVD, or other)
The following figures provide a high-level overview. Details of each step follow.
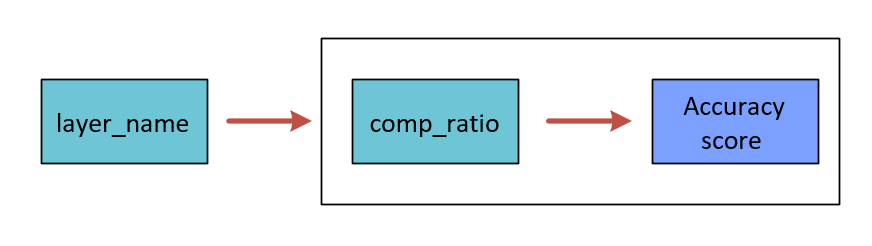
where the eval dictionary consists of per-layer sets of compression/accuracy maps:
Per-layer exploration
Per-layer exploration produces a column of scores over a range of compression ratios for each compressible layer. Each score represents the overall network performance value with the layer compressed at the specified ratio while all other layers are left unmodified. This collection of columns comprises the Evaluation Dictionary.
The figure below shows a model with 4 layers and 10 compression-ratio candidates (the default). The Evaluation Dictionary omits the eval score for the baseline compression ratio of 1.0 (for which the score is always 1.0).
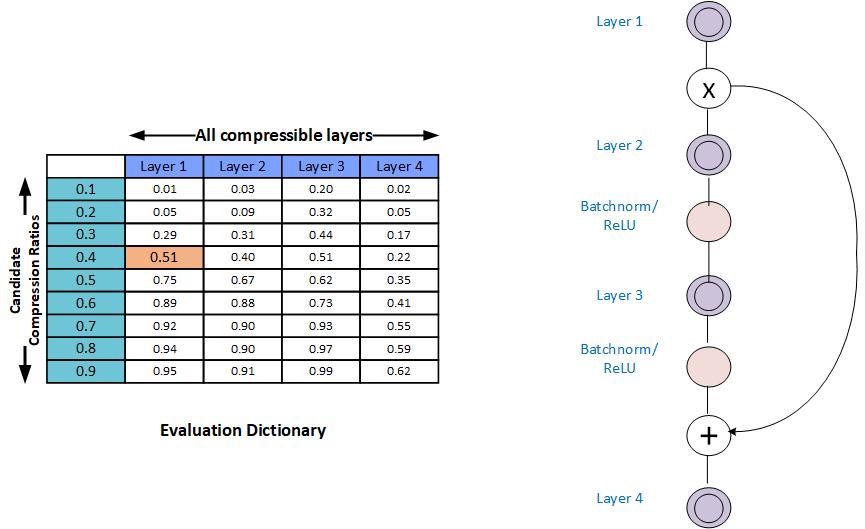
Monotonic Fit: In some cases the model performance does not increase monotonically with increasing compression ratio. To help with the greedy selection procedure, AIMET can fit a monotonically increasing curve to the model-performance numbers. This functionality is disabled by default.
Compression ratio selection
Compression ratio selection takes into account:
The target compression ratio
The evaluation function
The Evaluation Dictionary
The compression method (Spatial SVD, Channel Pruning)
Assuming a constant accuracy, the compression ratio selection algorithm calculates the compression ratio for every layer by interpolating from the layer’s column in the Evaluation Dictionary. It then calculates the total cost of the model based on the compression method (Spatial SVD, Channel Pruning) and evaluates whether the model meets the compression ratio target. If the solution is acceptable, it returns a list of selected compression ratios for all layers.
The following figure illustrates how the compression ratio for each layer can be different for a given accuracy.
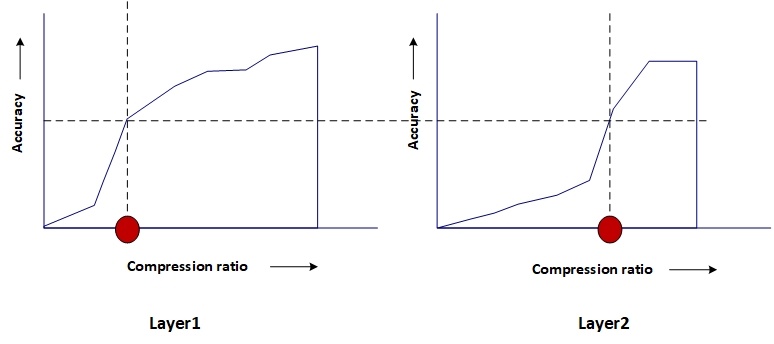
As suggested by the figure, the algorithm picks a lower compression ratio (higher compression) for layers that are more compressible and vice versa. For the less compressible layer (layer 2) the accuracy falls drastically with greater compression.