AIMET model quantization
Models are trained on floating-point hardware like CPUs and GPUs. However, when you run these models on quantized hardware with fixed-precision operations, the model parameters must be fixed-precision. For example, when running on hardware that supports 8-bit integer operations, the floating point parameters in the trained model need to be converted to 8-bit integers.
For some models, reduction to 8-bit fixed-precision introduces noise that causes a loss of accuracy. AIMET provides techniques and tools to create quantized models that minimize this loss of accuracy.
Use cases
This section briefly describes how AIMET’s quantization features apply to typical use cases.
- Quantization simulation
AIMET enables you to simulate running models on quantized targets. This helps you estimate on-target accuracy without requiring you to move the model to a quantized target platform.
A quantization simulation workflow is illustrated here:
- Post-training quantization (PTQ)
PTQ techniques make a model more quantization-friendly without requiring model retraining or fine-tuning. PTQ is recommended as a first step in a quantization workflow because:
PTQ does not require the original training pipeline; an evaluation pipeline is sufficient
PTQ requires only a small, unlabeled dataset for calibration
PTQ is fast and easy to use
The PTQ workflow is illustrated here:
With PTQ techniques, model accuracy may still be reduced. In such cases, fine-tuning is recommended.
- Quantization-aware training (QAT) and fine-tuning
QAT enable you to fine-tune a model with quantization operations inserted in the network graph. In effect, it makes the model parameters robust to quantization noise.
Compared to PTQ, QAT requires a training pipeline and dataset and takes longer because it needs some fine-tuning, but it can provide better accuracy, especially at low bitwidths.
A typical QAT workflow is illustrated here:
_aimet-quantization-features:
AIMET quantization features
- Quantization Simulation (QuantSim)
QuantSim modifies a model by inserting quantization simulation operations, providing a first-order estimate of expected runtime accuracy on quantized hardware.
- Quantization-Aware Training (QAT)
QAT enables fine-tuning of QuantSim model parameters by taking quantization into account.
Two modes of QAT are supported:
- Regular QAT
Fine-tuning of model parameters. Trainable parameters such as module weights, biases, etc. can be updated. The scale and offset quantization parameters for activation quantizers remain constant. Scale and offset parameters for weight quantizers will update to reflect new weight values after each training step.
- QAT with range learning
In addition to trainable module weights and scale/offset parameters for weight quantizers, scale/offset parameters for activation quantizers are also updated during each training step.
Post-Training Quantization
- Post-training quantization (PTQ) techniques
Post-training quantization techniques help improve quantized model accuracy without needing to re-train.
- AutoQuant
AIMET provides an API that integrates the post-training quantization techniques described below. AutoQuant is recommended for PTQ. If desired, individual techniques can be invoked using standalone feature specific APIs.
- Adaptive rounding (AdaRound)
Determines optimal rounding for weight tensors to improve quantized performance.
- Cross-Layer Equalization:
Equalizes weight ranges in consecutive layers. Implementation is variant-specific; see the API for your platform: PyTorch Keras ONNX
- BN re-estimation
Re-estimates Batch Norm layer statistics before folding the Batch Norm layers.
- Bias Correction (Deprecated)
Bias correction is deprecated. Use AdaRound instead.
Debugging and Analysis Tools
- Debugging and analysis tools
- QuantAnalyzer:
Automated debugging of the model to understand sensitivity to weight and/or activation quantization, individual layer sensitivity, etc.
- Visualizations:
Visualizations and histograms of weight and activation ranges.
AIMET quantization workflow
This section describes the recommended workflow for quantizing a neural network.
1. Prep and validate the model
Before attempting quantization, ensure that models are defined according to model guidelines. These guidelines depend on the ML framework (PyTorch or TensorFlow) that the model is written in.
PyTorch
PyTorch has two utilities to automate model complaince:
The Model Validator utility automates checking PyTorch model requirements
The Model Preparer utility automates updating model definition to align with requirements
In model prep and validation using PyTorch, we recommend the following flow:
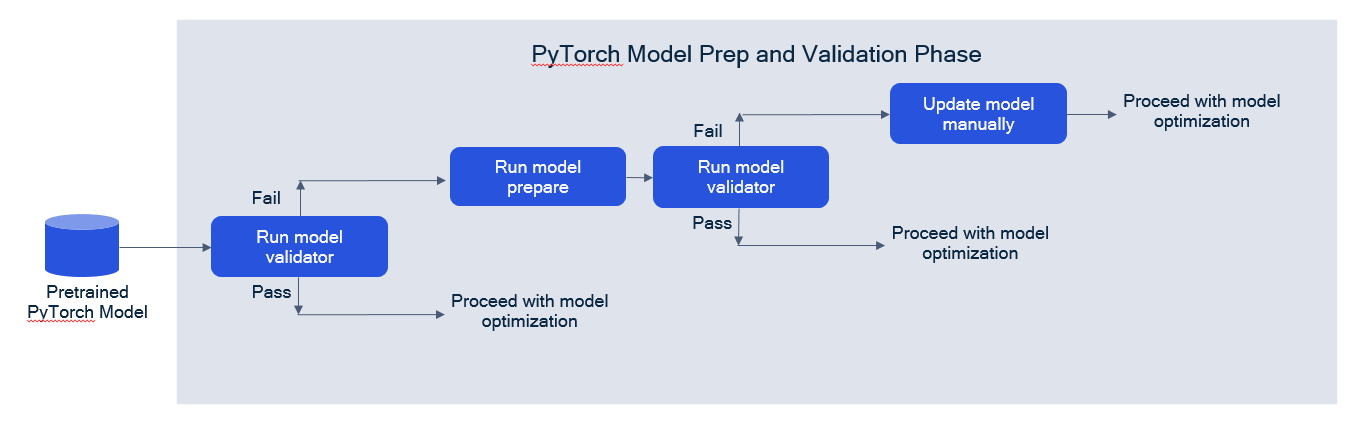
Use the Model Validator utility to check if the model can be run with AIMET. If validator checks fail, put Model Preparer in the pipeline and retry Model Validator. If the validator continues to generate warnings, update the model definition by hand.
For more information on Model Validator and Model Preparer, see AIMET PyTorch Quantization APIs.
2. Apply PTQ and AutoQuant
Apply PTQ techniques to adjust model parameters and make the model more robust to quantization. We recommend trying AutoQuant first. AutoQuant tries various other PTQ methods and finds the best combination of methods to apply. See :ref:`aimet-quantization-features`_.
3. Use QAT
If model accuracy is still not satisfactory after PTQ/AutoQuant, use QAT to fine-tune the model. See AIMET Quantization Features.
4. Export models
To move the model onto the target, you need:
A model with updated weights
An encodings file containing quantization parameters associated with each quantization operation
AIMET QuantSim can export both items. The exported model type differs based on the ML framework used:
.onnx for PyTorch
meta / checkpoint for TensorFlow
.h5 and .pb for Keras
The exact steps to export the model and encodings file depend on which AIMET Quantization features are used:
Calling AutoQuant automatically exports the model and encodings file.
If you use QAT, call .export() on the QuantSim object.
If you use lower-level PTQ techniques like CLE, first create a QuantSim object from the modified model, then call .export() on the QuantSim object.
Debugging
Applying AIMET Quantization features may involve some trial and error in order to find the best optimizations to apply on a particular model. If quantization accuracy does not seem to improve, see the debugging steps in the Quantization Diagnostics.